Signe Rätsep
Chief Specialist of the Legal Information and Judicial Training Department of the Supreme Court
The statistical data characterising the work of the Supreme Court[1] include the number of requests for proceedings submitted to the Supreme Court and matters reviewed by three types of court proceedings: civil, administrative court and offence proceedings. In constitutional review proceedings, data are gathered regarding the number of matters reviewed. Requests for proceedings are considered to include appeals in cassation, appeals against court rulings, applications for review and applications for procedural aid. Statistics on matters reviewed are kept according to the matters.[2]
Review of requests for proceedings in the chambers of the Supreme Court
According to law, the Supreme Court has the right to decide whether it opens proceedings with regard to a request in order to ensure the legitimacy of the judgments of courts of lower instance, harmonise case law or develop procedural law.
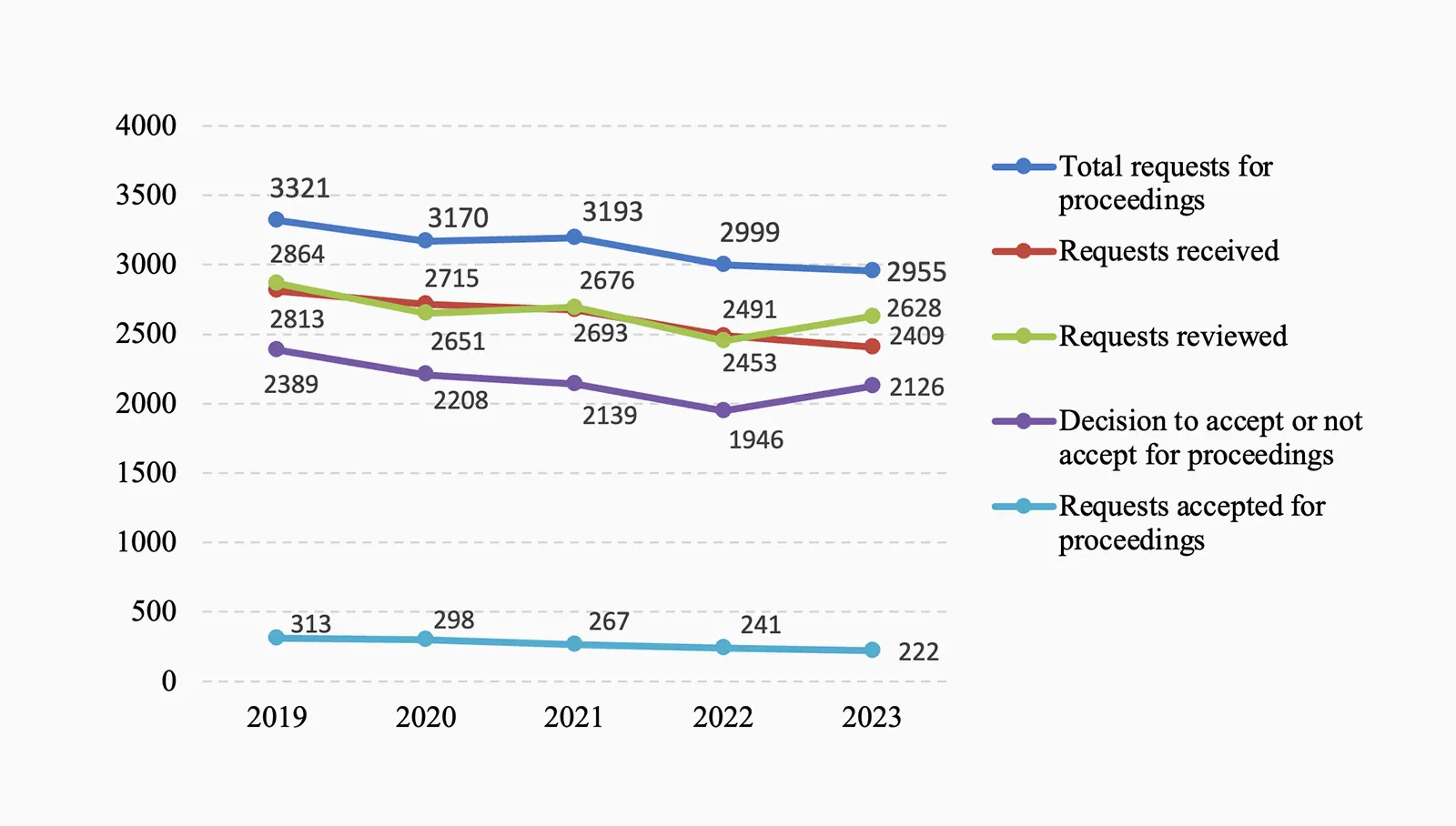
As can be seen from Figure 1, 10% of all requests in which the Supreme Court decided on acceptance or rejection were accepted in 2023 (222 of 2126 requests). By comparison, 13% of requests were accepted in 2019 and 2020, and 12% in 2021 and 2022.
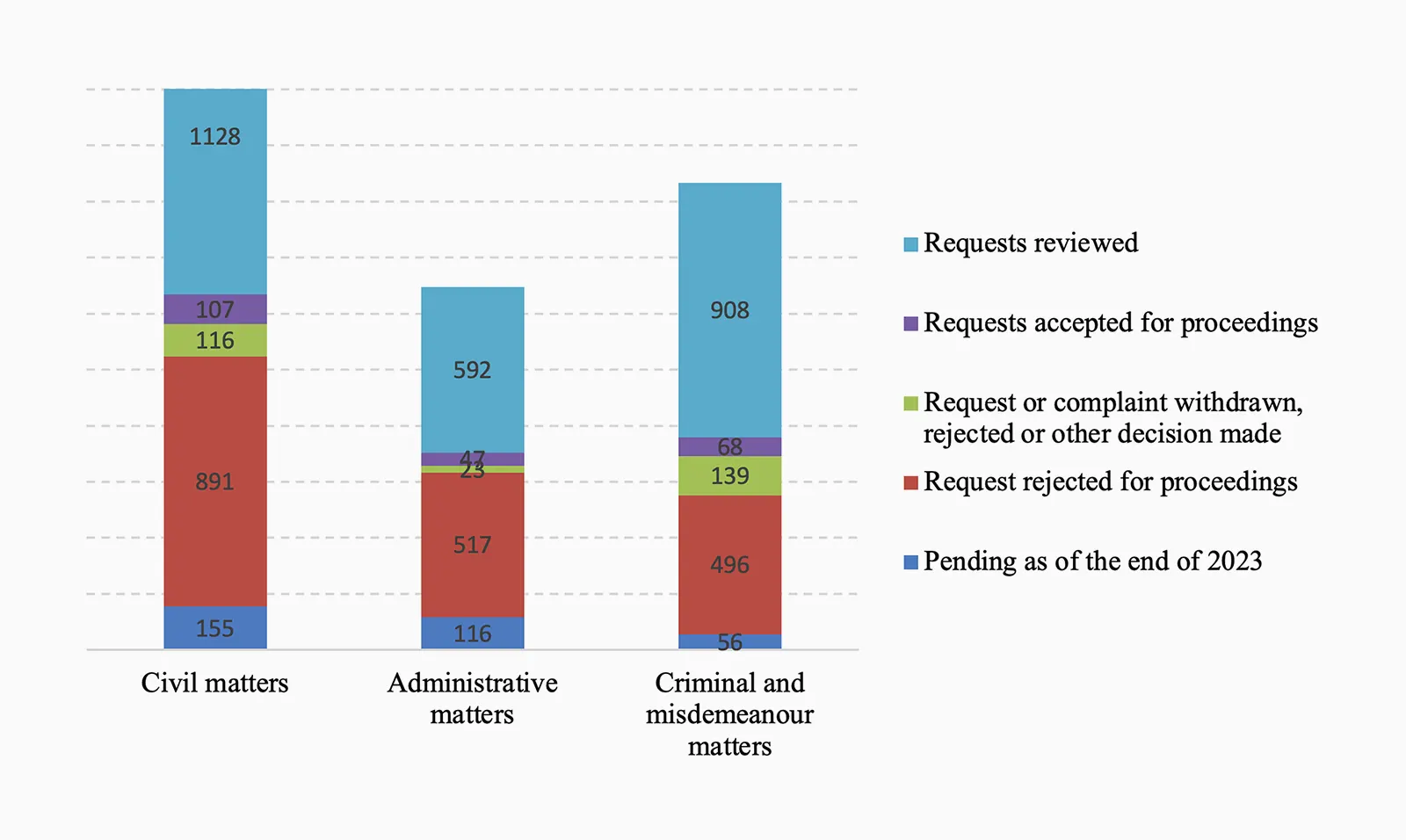
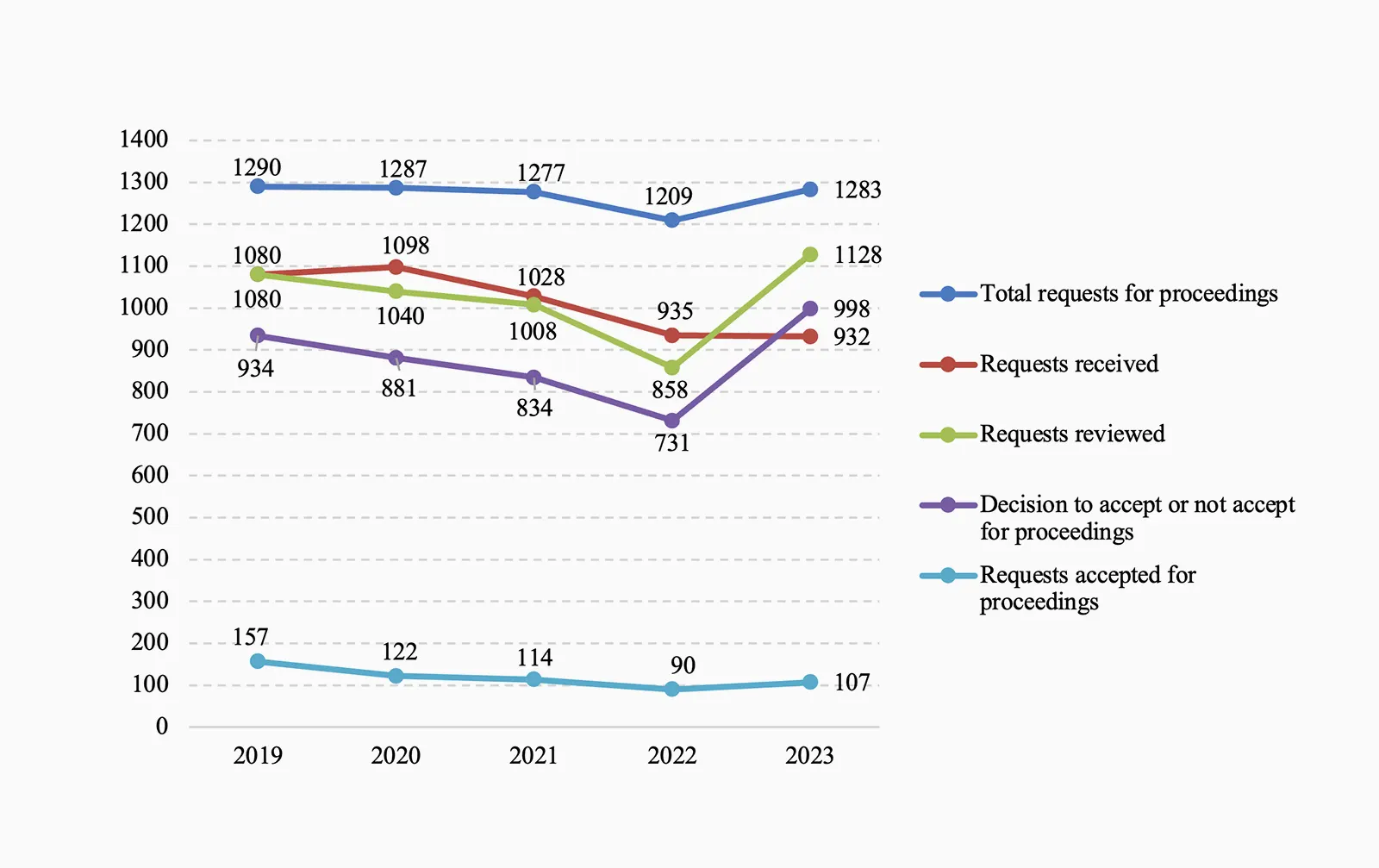
In the Civil Chamber, a total of 1283 requests for proceedings were pending (1209 in 2022), of which 932 were submitted in 2023. The chamber reviewed 1128 requests (858 in 2022). A decision on acceptance or rejection of the request was made in the case of 998 requests (731 in 2022), of which 107 (90 in 2022) were accepted.
In the Administrative Law Chamber, 708 requests for proceedings were pending in 2023 (2022: 743), of which 600 requests for proceedings were submitted in 2023. The Administrative Law Chamber reviewed 592 requests (634 in 2022), and a decision on acceptance or rejection of the request was made in the case of 564 requests (600 in 2022), of which 47 (71 in 2022) were accepted.
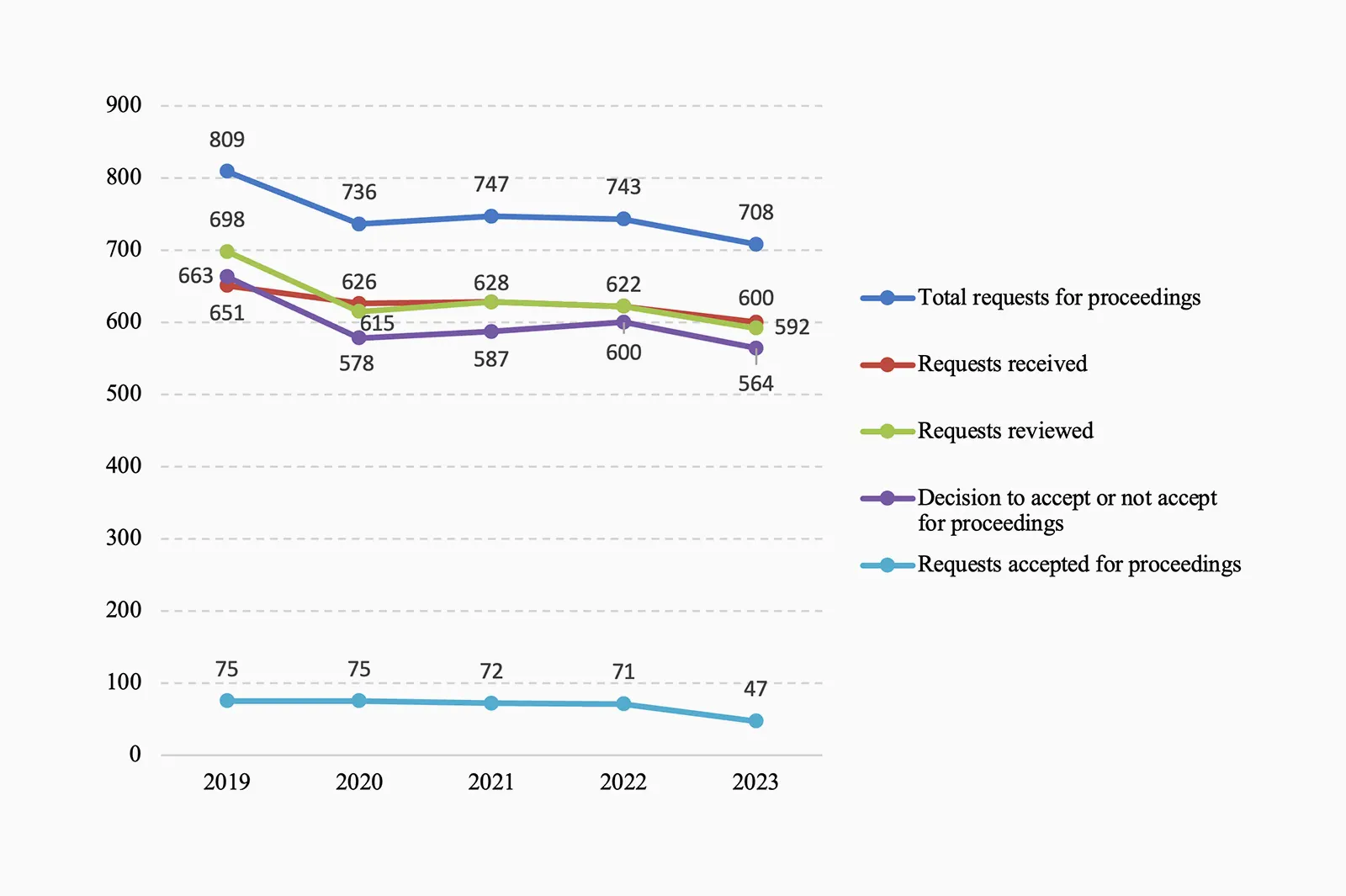
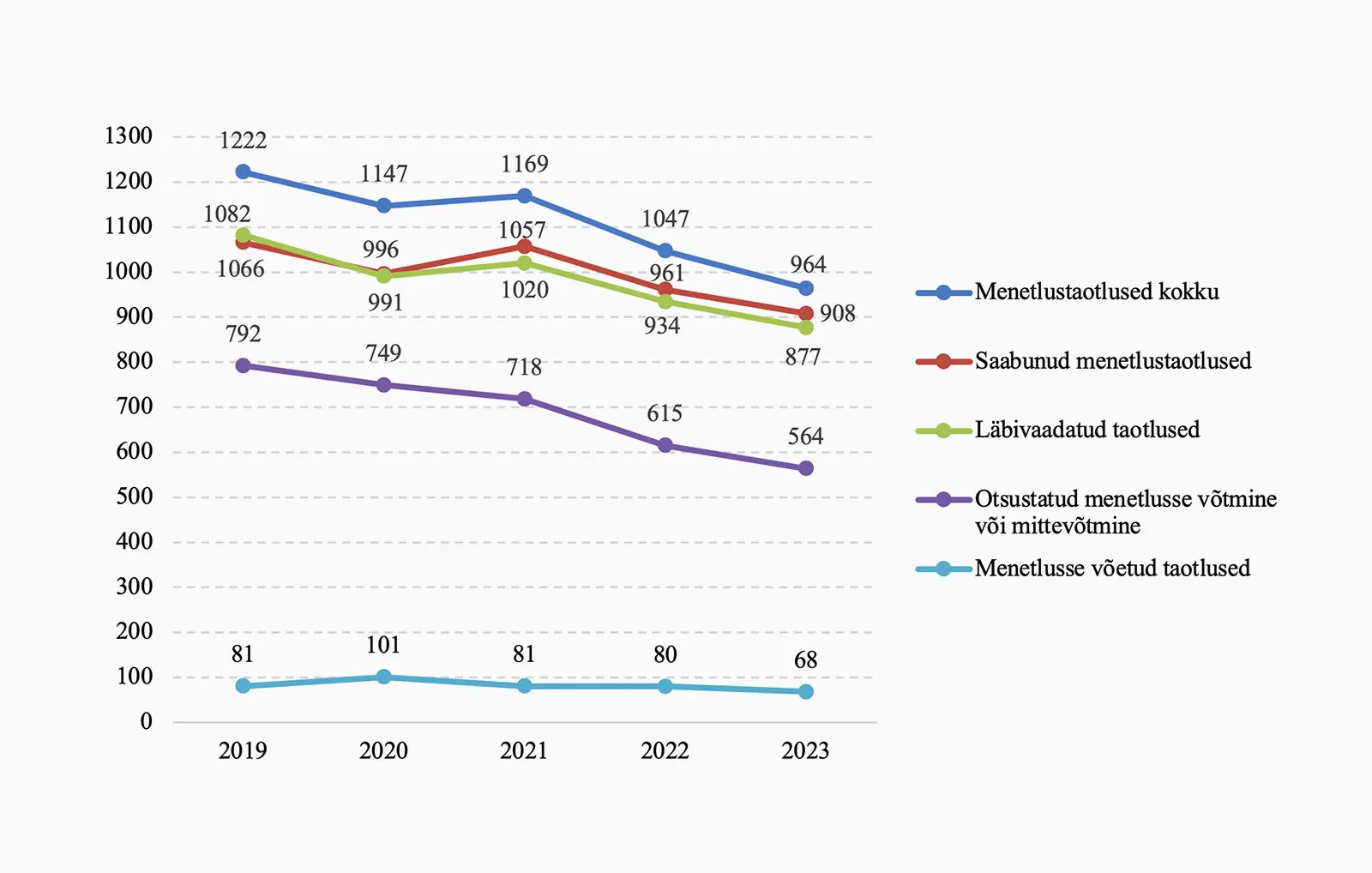
The Criminal Chamber had 964 requests in 2023 (2022: 1047), of which 877 requests were submitted in 2023. The chamber reviewed 908 requests (961 in 2022). A decision on acceptance or rejection of the request was made in the case of 564 requests (615 in 2022), of which 68 (80 in 2022) were accepted.
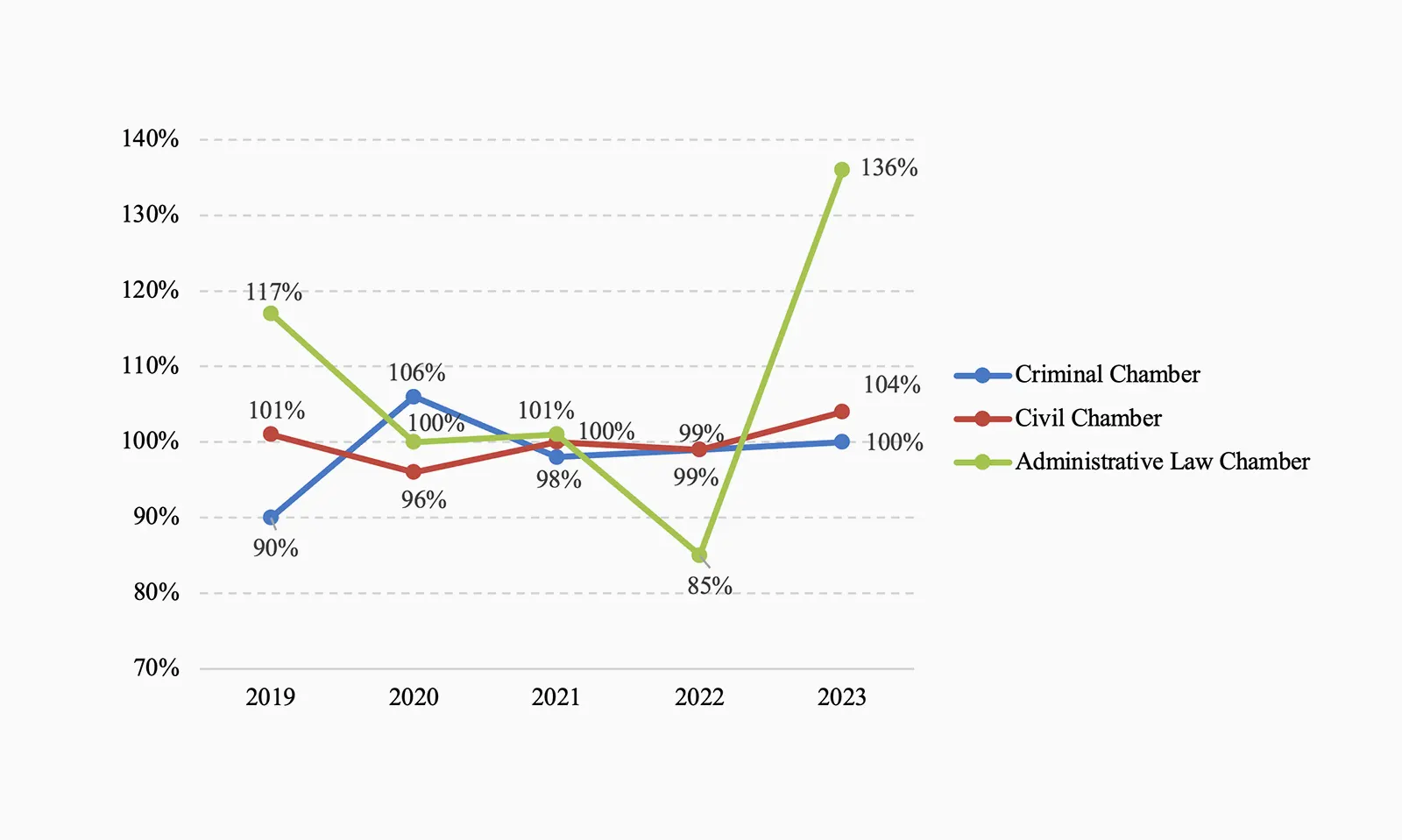
Results of the review of court matters in Supreme Court chambers
Constitutional review procedure
In 2023, 41 cases were reviewed in the constitutional review procedure. On one occasion, the Supreme Court en banc ruled on a constitutional review matter.
Review of court matters in the Criminal, Administrative Law and Civil Chamber
The Criminal Chamber ruled on 61 criminal and misdemeanour matters, 50 of them criminal and 11 misdemeanour matters. The Civil Chamber ruled on a total of 98 matters. The Administrative Law Chamber ruled on 60 administrative matters.

____________________________
[1] The data for 2023 have been taken from the Data and Analysis Environment of the Justice System (JAAK) as of 22 January 2024.
[2] More detailed data regarding the review of requests for proceedings and cases in the Supreme Court since 1993 are available on the website of the Supreme Court at https://www.riigikohus.ee/et/riigikohus/statistika.
[3] The explanations of figure captions are as follows: ‘Total requests for proceedings’ – requests for proceedings received during the reporting period, to which the matters pending at the end of the previous period, i.e. requests with respect to which no order had been made at the end of the previous period, have been added; ‘requests received’ – requests for proceedings whose date of receipt was in the reporting period; ‘requests reviewed’ – requests for proceedings with an undetermined time of arrival for which an order was made during the reporting period; ‘decision to accept or not accept for proceedings’ – requests for proceedings with respect to which an order on acceptance or rejection was made during the reporting period; ‘accepted for proceedings’ – requests for proceedings with respect to which an order on acceptance was made during the reporting period.
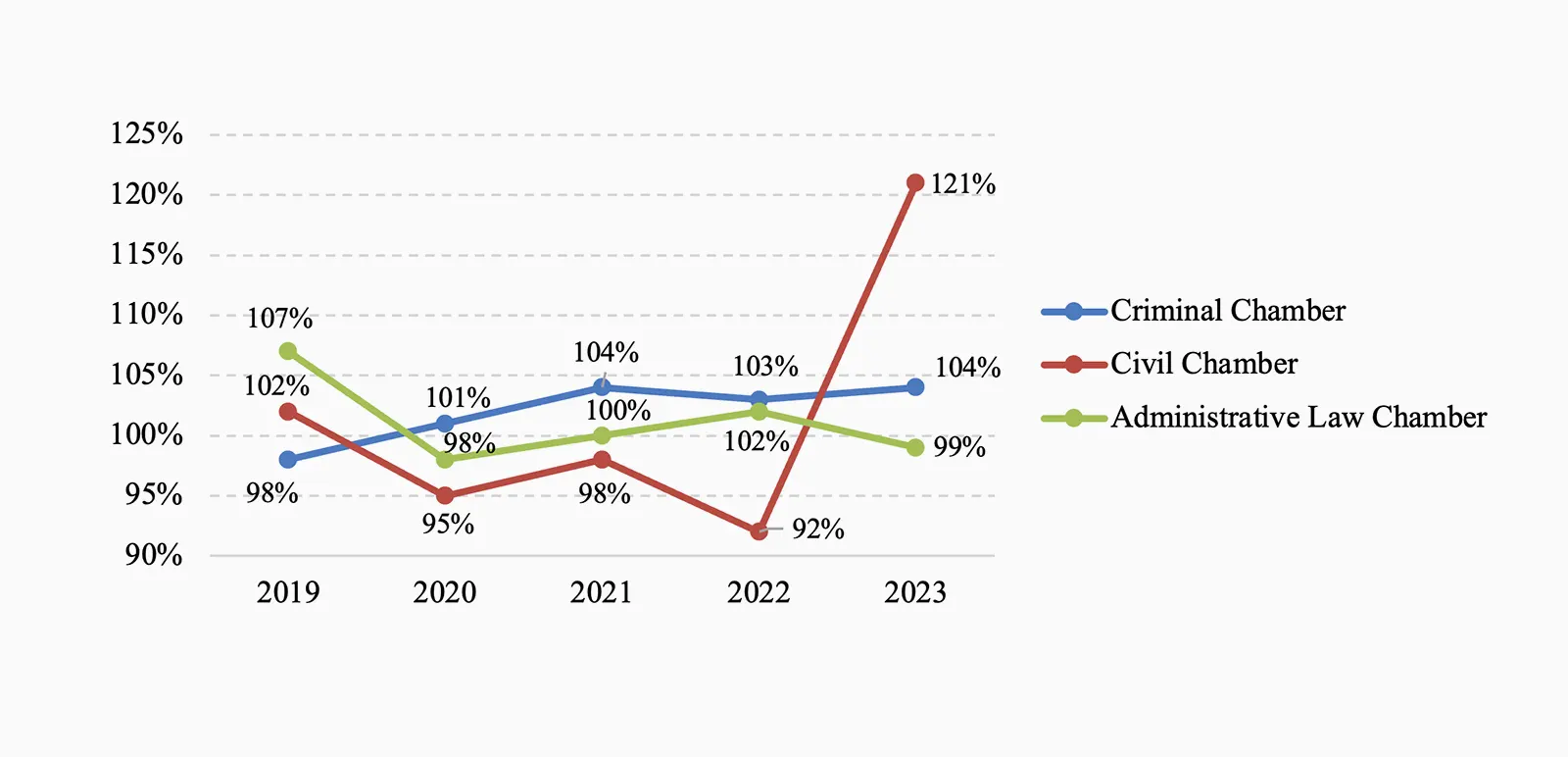
[4] Performance – the ratio of requests reviewed during the year to the number of requests received in the same period.
[5] Performance – the ratio of matters adjudicated during the year to the number of matters received for proceedings in the same period.



